We are grateful for the financial support for our research from the following agencies:
drug delivery
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a type of porous materials consisting of metal ions/clusters linked by organic ligands by forming a three-dimensional structure. Due to the high surface area, large pore size, and tunable chemical composition, MOFs have been used for many applications, including gas capture, storage and separation; catalysis; and biomedical uses.
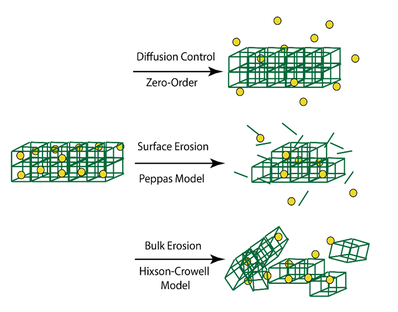
A group of Fe-containing MOFs have exhibited high drug loading capacities with low toxicity in various biological systems. We aim to design the next generation of drug-eluting stent coating with biodegradable Fe-containing MOF thin films to replace the current polymer coatings.
A group of Fe-containing MOFs have exhibited high drug loading capacities with low toxicity in various biological systems. We aim to design the next generation of drug-eluting stent coating with biodegradable Fe-containing MOF thin films to replace the current polymer coatings.
Methane Capture
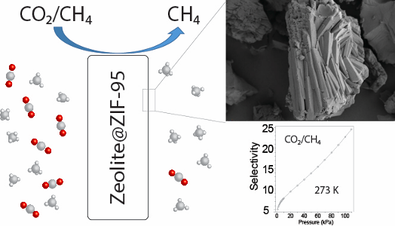
Methane is one of the primary greenhouse gases. A significant amount of methane has been released to the atmosphere over Arctic, and this process has been accelerated by global warming. At the same time, methane as the main component in natural gas is a superstar in alternative fuels. Trapping natural methane and transferring it into usable energy would be one way to unite these efforts. In this project, we study how to use hybrid MOFs to capture methane and separate it from other impurity gases.
MOF nanoparticles

The development of nano-scaled materials and nano-processing technology is becoming critically important. Due to the nature of the highly ordered pore structures of MOFs, the properties of nano-scaled MOFs may vary from their bulk materials. We explore ZIF-8 nanocrystals, composing of tetrahedrally coordinated zinc ions linked by 2-methylimidazolate ligands, due to their high stability in aqueous and the mild synthesis conditions. We have studied using ZIF-8 nanoparticles for water remediation. By incorporating other guest molecules, such as fluorophore, the resulted ZIF-8 composites can be used in other applications, such as explosive detection and cell labeling.
conductive and semiconductive 2d mofs
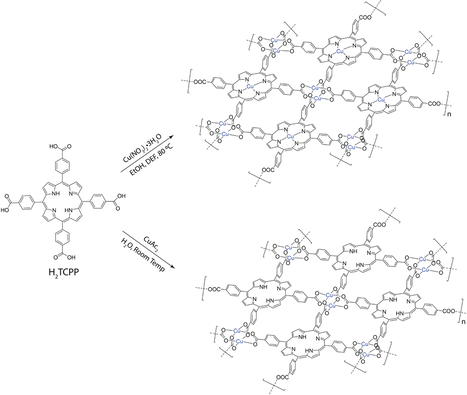
Recent advances in electrically conductive MOFs have led a range of applications in energy storage, chemical sensing, electrocatalysis, and fuel cells. 2D materials, such as graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides, have attracted a significant amount of attention due to their high charge mobility and unique electronic structures. This opens a new direction of making electronically conductive organic materials – 2D conductive MOFs. We focus on understanding the charge transport across a single layer and via a few multilayers of these 2D MOFs. We study the electrochemical properties of an ultrathin film of 2D MOFs that is formed at the interface of air and liquid by using a Langmuir trough. The horizontal charge transport of these ultrathin films is probed by microelectrode devices. The vertical charge transport of multilayers of these materials can be evaluated using a hanging mercury drop electrode (HMDE) system.






